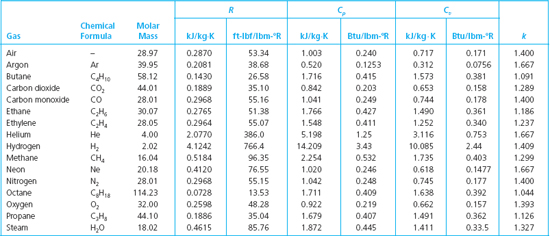
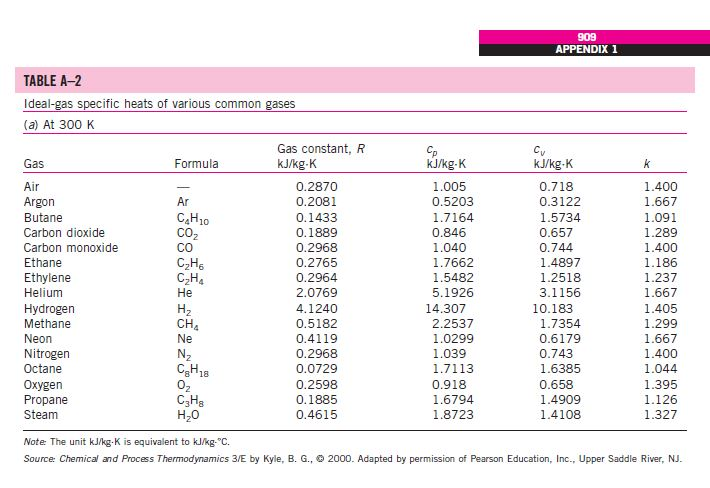
The molar mass of N2 is 280 gmol. The molar heat capacity at constant volume C V is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 mole of the gas by 1 K if.
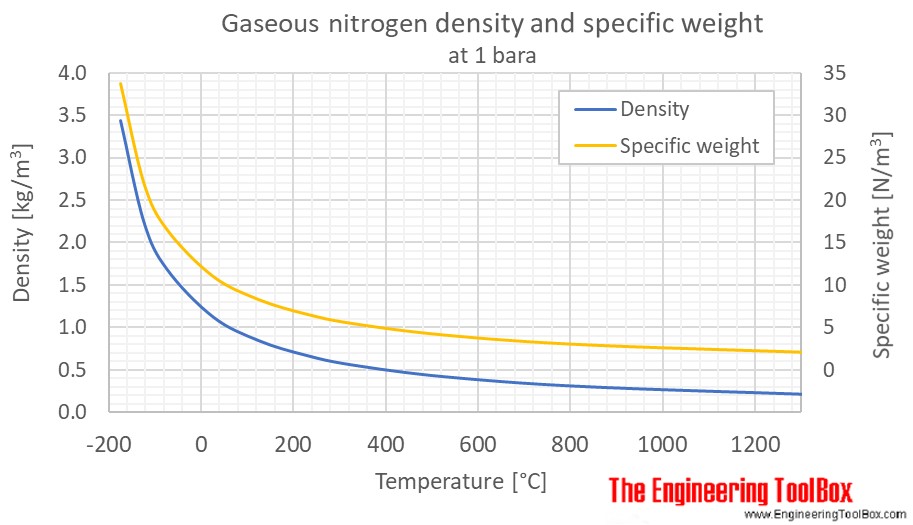
Nitrogen Density And Specific Weight Vs Temperature And Pressure
Values at 25 o C 77 o F 298 K and atmospheric pressure Follow the links below to get values for the listed properties of nitrogen at varying pressure and temperature.
. How much heat in J is required to raise the temperature from 50 K e 100 Kat concto nt pr Sonctant. Their SI units are Jkg K or Jmol K. Engineering Chemical Engineering QA Library Nitrogen gas has a heat capacity of 208 and 291 Jmol-C at constant volume and constant pressure respectively.
For the same amount of heat how many kilograms of 230C air would you be able to warm to 290C. How much heat in J is required to raise the temperature from 50 K to 100 K at constant pressure. Expert Answer Transcribed image text.
C p C_p C p - specific heat under constant pressure C v C_v C v - specific heat under constant volume. Textbook solution for University Physics 14th Edition 14th Edition Hugh D. The molar mass of N2 is 280 gmol DC ΟΙ ΑΣΦ i.
How much work is done by the gas in the constant volume process. Nitrogen is an inert neutral and colorless gas. This ratio γ 166 for an ideal monoatomic gas and γ 14 for air which is predominantly a diatomic gas.
This difference is particularly notable in gases where values under constant pressure are typically 30 to 667 greater than those at constant volume. C j kgk request answer part b you warm 130 kg of water at a constant volume from 220 c to 285 c in a kettle. B You warm 110 kg of water at a constant volume from 175 C to 285 C in a kettle.
Compute the specific heat capacity at constant volume of nitrogen n2 gas. Young Chapter 18 Problem 1839E. Submit Previous Answers Correct Part B 0 You warm 180 kg of water at a constant volume from 200C to 320C in a kettle.
Specific heat of Nitrogen Gas - N2 - at temperatures ranging 175 - 6000 K. The ratio of the specific heats γ C P C V is a factor in adiabatic engine processes and in determining the speed of sound in a gas. Hence the heat capacity ratio of gases is typically between 13 and 167.
49 rows The specific heat specific heat capacity at constant pressure and constant. The specific heat capacity at constant pressure c p is always greater than that at constant volume c v since if the volume of the gas increases work must be done by the gas to push back the surroundings. How much heat in J is required to raise the temperature from 50 K to 100 K at constant pressure.
The molar specific heat of nitrogen at constant volume is 4952 calmolK and that at constant pressure is 6933 calmolK. This is a closed system since no mass enters or. We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts.
K Submit Request Answer Part B You warm 185 kg of water at a constant volume from 220C to 320 C in a kettle. Compute the specific heat capacity at constant volume of nitrogen N_2 gas. A Compute the specific heat capacity at constant volume of nitrogen N2 gas.
1 kcal 41868 J 4269 kp m 1163x10-3 kWh 3088 ft lbf 39683 Btu 1000 cal Sponsored Links. The molar mass of n2 is 280 gmol. For the same amount of heat how many kilograms of 190 degree C air would you be able to warm to 320 degree C.
You warm 140 kg of water at a constant volume from 190 degree C to 320 degree C in a kettle. Dry air normal conditions 0C and 101325 hPa-. B You warm 100 kg of water at a constant volume of 100 L from 200 C to 300 C in a kettle.
Nitrogen gas has a heat capacity of 208 and 291 Jmol-at constant volume and constant pressure respectively. Sponsored Links Approximate molar specific heats at constant volume at room temperature for some common gases. The molar mass of N_2 is 280 gmol.
The molar mass of N 2 is 280 gmol. Density and specific weight Dynamic and kinematic viscosity Prandtl number Specific heat heat capacity Thermal conductivity Thermal diffusivity. For a constant volume process with a monoatomic ideal gas the first law of thermodynamics gives.
For the same amount of heat how many kilograms of 220 c air would you be able to warm to 285 c. The molar mass of N2 is 280 gmol. The molar mass of N2 is 280 gmol.
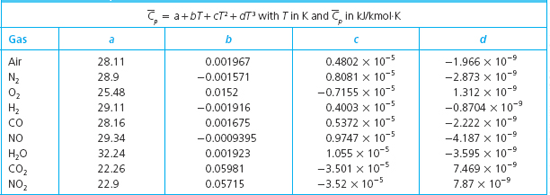
At high temperatures above 1500 K dissociation becomes appreciable and pressure is a significant variable. Two specific heats are defined for gases constant volume cv and constant pressure cp. C P C V R u R u molar massR Molar mass of nitrogen 21428 For N 2 R u 28R C P C V.
The values above apply to undissociated states. A Compute the specific heat capacity at constant volume of nitrogen N2 gas. Due to the high compressibility of gases two values of specific heat are given in their case.
Cv specific heat for gas in a constant volume process kJkgK dT change in temperature K Specific heat cv varies with temperature but within moderate temperature changes the specific heat - cv - can be regarded as constant. Part A Compute the specific heat capacity at constant volume of nitrogen N2 gas. 2020-11-13 by Nick Connor Nitrogen Specific Heat Specific heat of Nitrogen is 104 Jg K.
Denote the specific heats of nitrogen per unit mass at constant pressure and constant volume respectively then A C p C v 28R B C p C v 14R C C p C v R D C p C v 28R Medium JEE Mains Solution Verified by Toppr Correct option is A For any gas. According to the first law of thermodynamics for a constant volume process with a monatomic ideal gas the molar specific heat will be. Express your answer in joules per kilogram per kelvin.
Specific heat or specific heat capacity is a property related to internal energy that is very important in thermodynamics. Molar specific heats for some common gases at constant volume. For the same amount of heat how many kilograms of 175 C air would you be able to warm to 285 C.
Cv 32R 125 Jmol K because U 32nRT. C 741 J kg K. Part A Compute the specific heat capacity at constant volume of nitrogen N2 gas.
We are given that liquid HCN Specific gravity 10oC4oC 12975. Nitrogen gas has a heat capacity of 208 and 291 Jmol-C at constant volume and constant pressure respectively. Specific Heat of Gases Enthalpy For an ideal gas the enthalpy - h - is a function of temperature.
Nitrogen accounts for 78 of the atmospheric air volume. 741 J kgk B You warm 155kg of water at a constant volume from 230C to 290C in a kettle. Compressibility is the property.
Problem 39 Hard Difficulty a Compute the specific heat at constant volume of nitrogen N 2 gas and compare it with the specific heat of liquid water.
Solved Specific Heats At Constant Pressure And Volume Are Chegg Com
Solved Nitrogen Is Heated From 20 C To 500 C Calculate The Chang Chegg Com
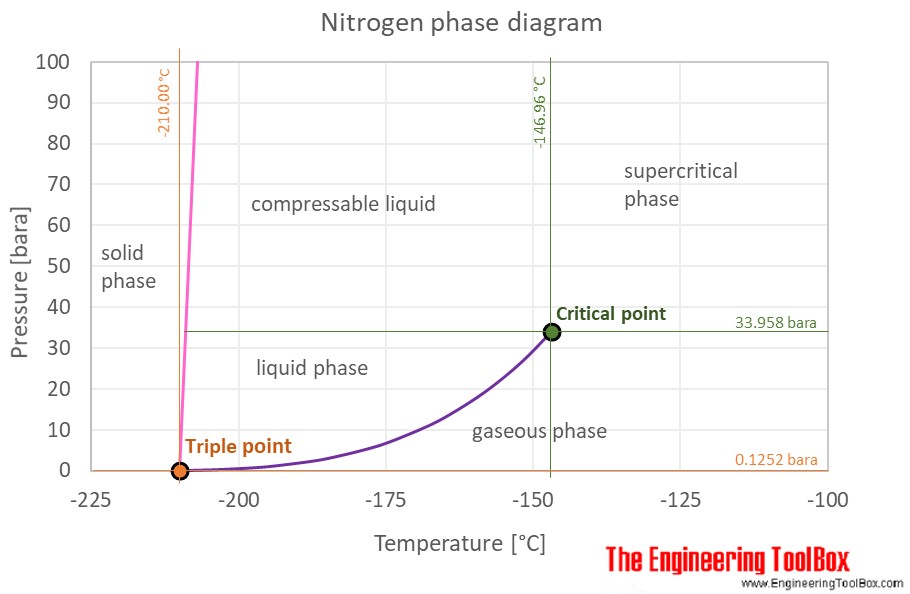
Nitrogen Thermophysical Properties

Solved Nitrogen Is Heated From 20 C To 500 C Calculate The Chang Chegg Com
0 Comments